Companies exist within a wider context of information,
finances, resources, and sociological networks that impact their long-term health.
Successful companies can formalize and embrace this interconnected nature to
develop enhanced levels of performance. They are semi-open systems that can take
in information, transform it into something new, and contribute to their
environment while ensuring they are retaining healthy profit margins.
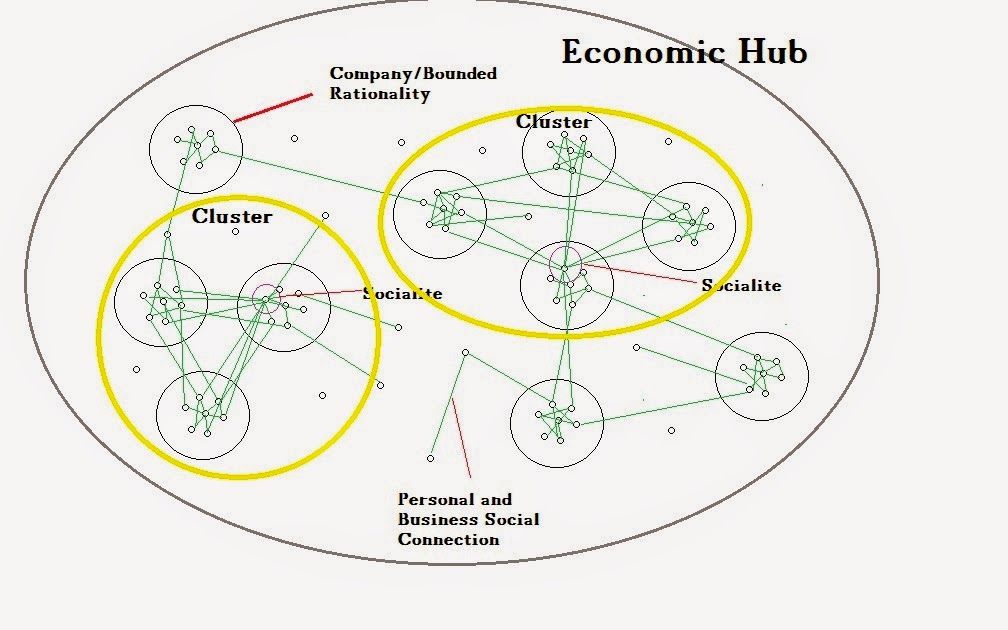
Hubs are made of clusters of competencies that make up the back bone of local human capital. They form when
businesses with similarities work in tandem and share common characteristics. We can see how clusters are formed
around competencies in science, entrepreneurship, art, manufacturing, or just
about any other industry.
Clusters have socialites who foster and push network creation.
Socialites pass out cards, attend meetings, make phone calls, and connect
resources and finances to create new things. They are the entrepreneurs and
pro-social developers that use their networks to solve problems. Such
individuals are capable of changing markets by putting the right people in
touch with each other.
Companies have something called bounded rationality.
This is where people band together to form an entity that produces new products/services. They share similarities in knowledge, culture, and competencies
bounded into a single business for financial gain. All companies have a level
of bounded rationality where members think and act alike.
Hubs exist within a regional, national, and global
marketplace. They are places where resources are converted into innovative
products. A hub is defined by the types of clusters/competencies it has within
in ranks. Clusters work together to create a type of synergy that is unique to
that particular hub and all the elements that come define it.
The ease by which people act and interact with each
other determines the success of hubs. This interaction can be defined by
financial, knowledge, and social based goal directed behavior. Development of
hubs requires a level of improvement in the ease and speed of transference.
This is one reason why new technology can be a game changer. Strong hubs continually
develop new knowledge, financial efficiencies, and production outputs.